Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
Tags
- 코딩테스트합격자되기
- redux-toolkit
- SW
- 테코테코
- useDispatch
- react-redux
- Python
- react
- react-router
- createSlice
- maeil-mail
- 매일메일
- redux-saga
- 항해플러스
- java
- 알고리즘
- C++
- JavaScript
- axios
- 자바
- programmers
- sw expert academy
- 프로그래머스
- 항해99
- redux
- 이코테
- Get
- 리액트
- Algorithm
- json-server
Archives
- Today
- Total
Binary Journey
[Algorithm] 이분 매칭 (Bipartite Matching) 본문
Algorithm/알고리즘 스터디(2021.07)
[Algorithm] 이분 매칭 (Bipartite Matching)
binaryJournalist 2021. 11. 1. 21:24반응형
인프런 32강에 대한 리뷰다
[무료] 알고리즘의 개요와 실습 환경 구축 - 인프런 | 강의
알고리즘을 배우며, 실무에서는 알고리즘이 어떻게 활용되는지 알아봅니다., [임베딩 영상] 알고리즘의 개요와 실습 환경 구축 알고리즘은 문제를 해결하는 절차입니다.입력, 출력, 유한성, 명
www.inflearn.com
이분 매칭은 쉽게 말하자면 A와 B라는 두 집합을 가장 효율적으로 매칭하는 방법의 알고리즘이다.
네트워크 플로우 때 음의 유량을 응용한 방법이라고도 볼 수 있다.
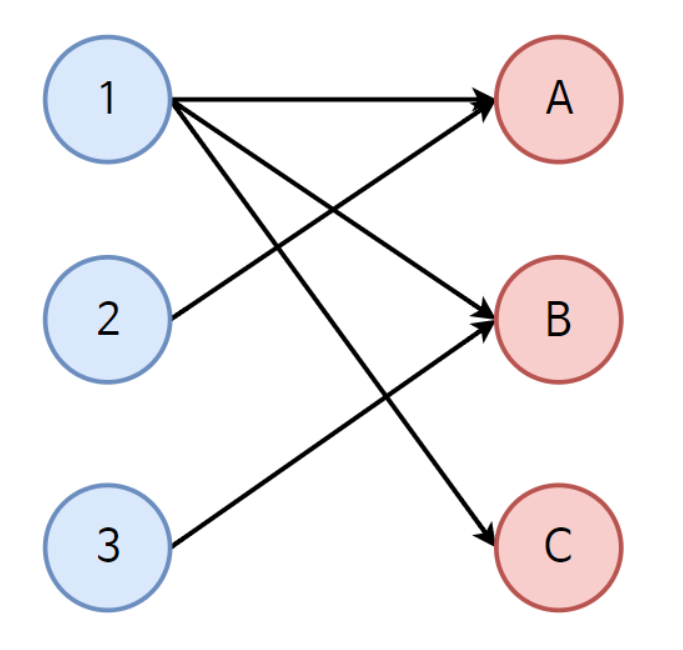
위 그림을 예를 들어 임의의 사람 1, 2, 3 이 A, B, C와 매칭한다고 했을 때 1, 2, 3을 최대로 만족할 수 있는 방법을 구하는 것이다.
1 은 먼저 A 와 매칭되지만 2도 2의 유일한 선택지인 A와 매칭되므로 1 은 원 상태로 되돌아와 다른 선택지로 존재하는 B 를 선택한다.
그러나 3의 유일한 선택지도 B이므로 A는 다시 원상태로 돌아와 남은 선택지인 C로 매칭된다.
이분 매칭은 DFS를 응용한다.
강의에서 나온 소스이다
**C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define MAX 101
using namespace std;
vector<int> a[MAX];
int d[MAX];
bool c[MAX];
int n = 3, m, s;
// 매칭 성공: True, 실패: False
bool dfs(int x) {
// 연결된 모든 노드에 대해서 들어갈 수 있는지 시도
for (int i = 0; i < a[x].size(); i++) {
int t = a[x][i];
// 이미 처리한 노드는 더 이상 볼 필요가 없음
if (c[t]) continue;
c[t] = true;
// 비어있거나 점유한 노드에 더 들어갈 공간이 있는 경우
if (d[t] == 0 || dfs(d[t])) {
d[t] = x;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main(void) {
a[1].push_back(1);
a[1].push_back(2);
a[1].push_back(3);
a[2].push_back(1);
a[3].push_back(2);
int count = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fill(c, c + MAX, false);
if(dfs(i)) count++;
}
printf("%d개의 매칭이 이뤄졌습니다.\n", count);
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
if(d[i] != 0) {
printf("%d -> %d\n", d[i], i);
}
}
return 0;
}
** Python
max = 101
vector = [[] for i in range(max + 1)]
dept = [ 0 for i in range(max + 1)]
# visited = [ False for i in range(max + 1)]
n = 3
m = 0
def dfs(x, visited):
for v in vector[x]:
t = v
if visited[t]: continue
visited[t] = True
if dept[t] == 0 or dfs(dept[t], visited):
dept[t] = x
return True
return False
def main():
vector[1].append(1)
vector[1].append(2)
vector[1].append(3)
vector[2].append(1)
vector[3].append(2)
count = 0
# visited = [ False for i in range(max + 1)]
for i in range(1, n + 1):
visited = [ False for i in range(max + 1)]
if dfs(i, visited): count += 1
print(f'{count}개의 매칭이 이뤄졌습니다.')
for i in range(1, max + 1):
if not dept[i] == 0:
print(f'{dept[i]} -> {i}')
main()
반응형
'Algorithm > 알고리즘 스터디(2021.07)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm] 단순 문자열 매칭 알고리즘 (0) | 2021.11.22 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm] 위상정렬 문제풀이 (1) | 2021.11.16 |
| [Algorithm] 네트워크 플로우 (Network Flow) (0) | 2021.10.25 |
| [Algorithm] 강한 요소 결합 (Strongly Connected Component, SCC) (0) | 2021.10.24 |
| [Algorithm] Topology Sort (위상 정렬) (0) | 2021.10.17 |