[Algorithm] 심화 정렬 알고리즘 문제 풀이 (백준 1181, 1431, 10989)
[무료] 알고리즘의 개요와 실습 환경 구축 - 인프런 | 강의
알고리즘을 배우며, 실무에서는 알고리즘이 어떻게 활용되는지 알아봅니다., [임베딩 영상] 알고리즘의 개요와 실습 환경 구축 알고리즘은 문제를 해결하는 절차입니다.입력, 출력, 유한성, 명
www.inflearn.com
13강에 대한 리뷰이다.
강의에서는 이론만으로는 코딩테스트나 실전에 적용하기 어려우니 실습이 필요하다고 한다.
그래서 백준 문제를 푼다.
1. 백준 1181 단어 정렬
: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1181
1) C++
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
string a[20000];
int n;
bool compare(string a, string b) {
// 길이가 짧은 순서 우선
if (a.length() < b.length()) {
return 1;
} else if (a.length() > b.length()) {
return 0;
}
// 길이가 같은 경우 (사전순)
else {
return a < b;
}
}
int main(void) {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a, a + n, compare);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 동일한 단어는 패스
if(i > 0 && a[i] == a[i - 1]) {
continue;
} else {
cout << a[i] << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
2) Javascript
백준에는 자바스크립트를 지원하지 않지만 만약 있다면 이렇게 작성했을 것이다.
function main() {
const n = prompt();
if (isNaN(Number(n))) return;
const input = prompt();
let array = input.split("\r\n");
array.sort((a, b) => {
if (a.length === b.length) return (a < b) ? -1 : 1
else return a.length - b.length;
});
for (const word of [...new Set(array)]) {
console.log(word);
}
}
엔터 입력값 때문에 \n 이 아닌 \n\r 로 split 을 했다.
그리고 C++ 도 sort 함수 이용했길래 나도 javascript 의 sort 를 이용하였고 조건은 직접 넣었다.
중복 제거는 중복값을 허용하지 않는 Set를 이용하였다.
요소가 숫자인 경우 sort((a, b) => a - b) 를 사용하지만 문자열의 경우 그냥 sort()를 쓰면 되지만
위 경우 숫자(문자열의 길이)와 문자열 비교이기 때문에 문자열 비교 조건에서는 -1, 0 ,1 를 리턴해줘야 한다.
그래서 return (a < b) ? -1 : 1 이 된 것이다.
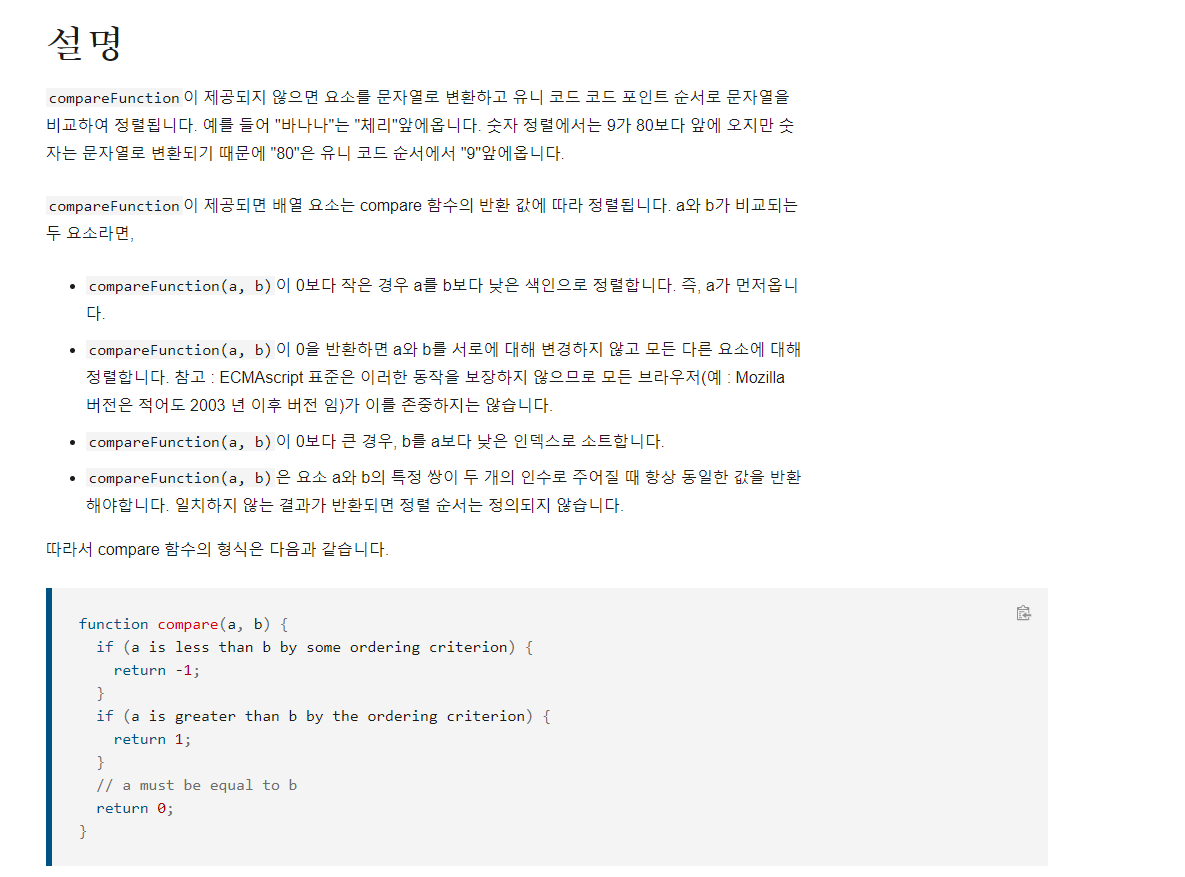
javascript의 Array.sort() 를 더 알고 싶다면 아래 사이트를 참고
https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/sort
Array.prototype.sort() - JavaScript | MDN
sort() 메서드는 배열의 요소를 적절한 위치에 정렬한 후 그 배열을 반환합니다. 정렬은 stable sort가 아닐 수 있습니다. 기본 정렬 순서는 문자열의 유니코드 코드 포인트를 따릅니다.
developer.mozilla.org
3) Java
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String[] arr = new String[n];
sc.nextLine(); // 엔터 개행 버림
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextLine();
}
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<String>() {
public int compare(String a, String b) {
// if (a.length() < b.length()) {
// return 1;
// } else if (a.length() > b.length()) {
// return 0;
// } else {
// return a < b;
// }
if (a.length() == b.length()) {
return a.compareTo(b);
}
else {
return a.length() - b.length();
}
}
});
System.out.println(arr[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (!arr[i].equals(arr[i - 1])) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
}
java 에서도 Arrays.sort() 메소드를 이용하였다.
Arrays.sort() 의 경우 Comparator 를 이용하여 사용자 정의 정렬 조건을 만들 수 있다.
그리고 두 String을 비교하는 경우 길이를 각각 다를 때를 모두 조건으로 나누지 않고 a.length() - b.length() 를 쓰면 된다. 또한 String 사전적 정렬은 compareTo 메서드를 이용하면 된다.
Arrays.sort() 사용자정의 부분은 아래 블로그를 참고하였다.
https://st-lab.tistory.com/112
[백준] 1181번 : 단어 정렬 - JAVA [자바]
www.acmicpc.net/problem/1181 1181번: 단어 정렬 첫째 줄에 단어의 개수 N이 주어진다. (1≤N≤20,000) 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에 걸쳐 알파벳 소문자로 이루어진 단어가 한 줄에 하나씩 주어진다. 주어지는 문
st-lab.tistory.com
2. 백준 1431 시리얼번호
: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1431
1) C++
강의 그대로 따라하면 런타임 에러 난다.
동빈 나님 블로그 가보니까 소스가 조금 다름
강의에서도 블로그 소스가 이렇게 나오는데 왜 바로 안 쓰셨지
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector <string> v;
int getSum(string a) {
int length = a.length(), sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
// 숫자인 경우에만 더함
if (a[i] - '0' <= 9 && a[i] - '0' >= 0) {
sum += a[i] - '0';
}
}
return sum;
}
bool compare(string a, string b) {
// 길이가 짧은 순서 우선
if (a.length() != b.length()) {
return a.length() < b.length();
}
// 길이가 같은 경우 (글자에 포함된 숫자의 합이 더 작은 것이 우선)
else {
int aSum = getSum(a);
int bSum = getSum(b);
if (aSum != bSum) {
return aSum < bSum;
} else {
// 숫자 합까지 같다면 사전순
return a < b;
}
}
}
int main(void) {
cin >> n;
string input;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> input;
v.push_back(input);
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), compare);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << v[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2) Javascript
function getSum(word) {
return word.split("").reduce((acc, curr) => acc += (curr >= '0' && curr <= '9') ? +curr : 0, 0);
}
function main() {
const n = prompt();
if (isNaN(Number(n))) return;
const input = prompt();
let array = input.split("\r\n");
array.sort((a, b) => {
if (a.length === b.length) {
const aSum = getSum(a);
const bSum = getSum(b);
if (aSum === bSum) return a - b;
else return aSum - bSum;
} else {
return a.length - b.length;
}
});
for (let i = 0; i < Number(n); i++) {
console.log(array[i]);
}
}
나오는 순서는 동일한데 이 경우 A, 5까지 출력된다.
아마 getSum 부분에서 잘못된 거 아닐까 싶다.
getSum 에서 잘못한 게 아니고 처음에 개수 받는 부분을 고려하지 않고 전부 한 array 안에 받았다.
3) Java
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Main {
private static int getSum(String s) {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) >= '0' && s.charAt(i) <= '9') {
sum += s.charAt(i) - '0';
}
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String[] arr = new String[n];
sc.nextLine(); // 엔터 개행 버림
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextLine();
}
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<String>() {
public int compare(String a, String b) {
// if (a.length() < b.length()) {
// return 1;
// } else if (a.length() > b.length()) {
// return 0;
// } else {
// return a < b;
// }
if (a.length() == b.length()) {
if (getSum(a) == getSum(b)) {
return a.compareTo(b);
}
return getSum(a) - getSum(b);
}
else {
return a.length() - b.length();
}
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}
Java 소스는 1181번 문제와 크게 다르지 않다.
getSum 메서드의 charAt 이용하는 부분은 아래 블로그를 참고하였다.
[1431] 시리얼 번호 (자바8)
www.acmicpc.net/problem/1431 1431번: 시리얼 번호 첫째 줄에 기타의 개수 N이 주어진다. N은 1,000보다 작거나 같다. 둘째 줄부터 N개의 줄에 시리얼 번호가 하나씩 주어진다. 시리얼 번호의 길이는 최대 50
par3k.tistory.com
3. 백준 10989 수 정렬하기 3
: https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/10989
데이터의 개수가 매우 많은데 시간제한 + 범위 조건이 있기 때문에 계수 정렬을 이용한다.
1) C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
int a[10001];
int main(void) {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
a[x]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 10001; i++) {
while(a[i] != 0) {
printf("%d\n", i);
a[i]--;
}
}
return 0;
}
2) Javascript
function main() {
const n = prompt();
if (isNaN(Number(n))) return;
const number = Number(n);
const count = new Array(10001).fill(0);
const input = prompt();
input.split("\r\n").forEach((each, index) => count[each]++);
for(let i = 0; i < 10001; i++) {
while(count[i] > 0) {
console.log(i);
count[i]--;
}
}
}
3) Java
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = sc.nextInt();
int[] count = new int[10001];
sc.nextLine(); // 엔터 개행 버림
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) {
int x = sc.nextInt();
count[x]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < count.length; i++) {
while(count[i] > 0) {
System.out.println(i);
count[i]--;
}
}
}
}